Video
Trauma and Fracture Management in Companion Animals: Practical Insights for Veterinarians
Fracture management in dogs and cats requires a structured, stepwise approach beginning with patient stabilization and accurate diagnosis. Treatment decisions are guided by fracture classification, biomechanical principles, and individual patient factors. A range of fixation options—such as external coaptation, intramedullary devices, plates, and external skeletal fixators—allows veterinarians to tailor therapy to each case. Successful outcomes rely not only on precise surgical technique but also on effective pain management, aseptic handling, and comprehensive post-operative rehabilitation. Continuous monitoring, including radiographic follow-up, helps detect complications early and ensures optimal healing and functional recovery.
To deepen your understanding of feline fractures, explore this latest research study.
https://master-session-video.s3.ap-southeast-1.wasabisys.com/Dentalnet-VetNet/PDF/Dr.%20Kunal%20Dev%20Sharma.pdf
Related Experts
Related Contents
.jpg)
Article
Immunoprophylaxis and Vaccines for Lumpy Skin Disease in India
Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) is a capripoxvirus-induced viral disease affecting cattle and buffaloe...
.jpg)
Article
Lumpy Skin Disease in India: Diagnostic Challenges, Differential Diagnoses, and Laboratory Confirmation
Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) is a contagious viral disease of cattle caused by Lumpy Skin Disease Virus...

Article
Lumpy Skin Disease: From Clinical Signs to Field-Level Control
Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) is a highly contagious viral disease of cattle and buffaloes caused by the...

Article
Antimicrobial Resistance: Breaking Professional Silos to Protect the Future of Medicine
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has evolved into a critical global health problem affecting humans, a...

Article
Environmental Health, Animal Health, Human Health – Connecting the Missing Links
The health of humans, animals, and the environment is increasingly understood to be i...

Article
Zoonotic Diseases Without Borders: Why One Health Collaboration Starts with Veterinarians
Zoonotic diseases, those that are transmitted between animals and humans, represent some of the grea...

Article
From Clinics to Communities – The Veterinarian’s Expanding Role in One Health
In the evolving landscape of global health, veterinarians are no longer confined to treating&nb...
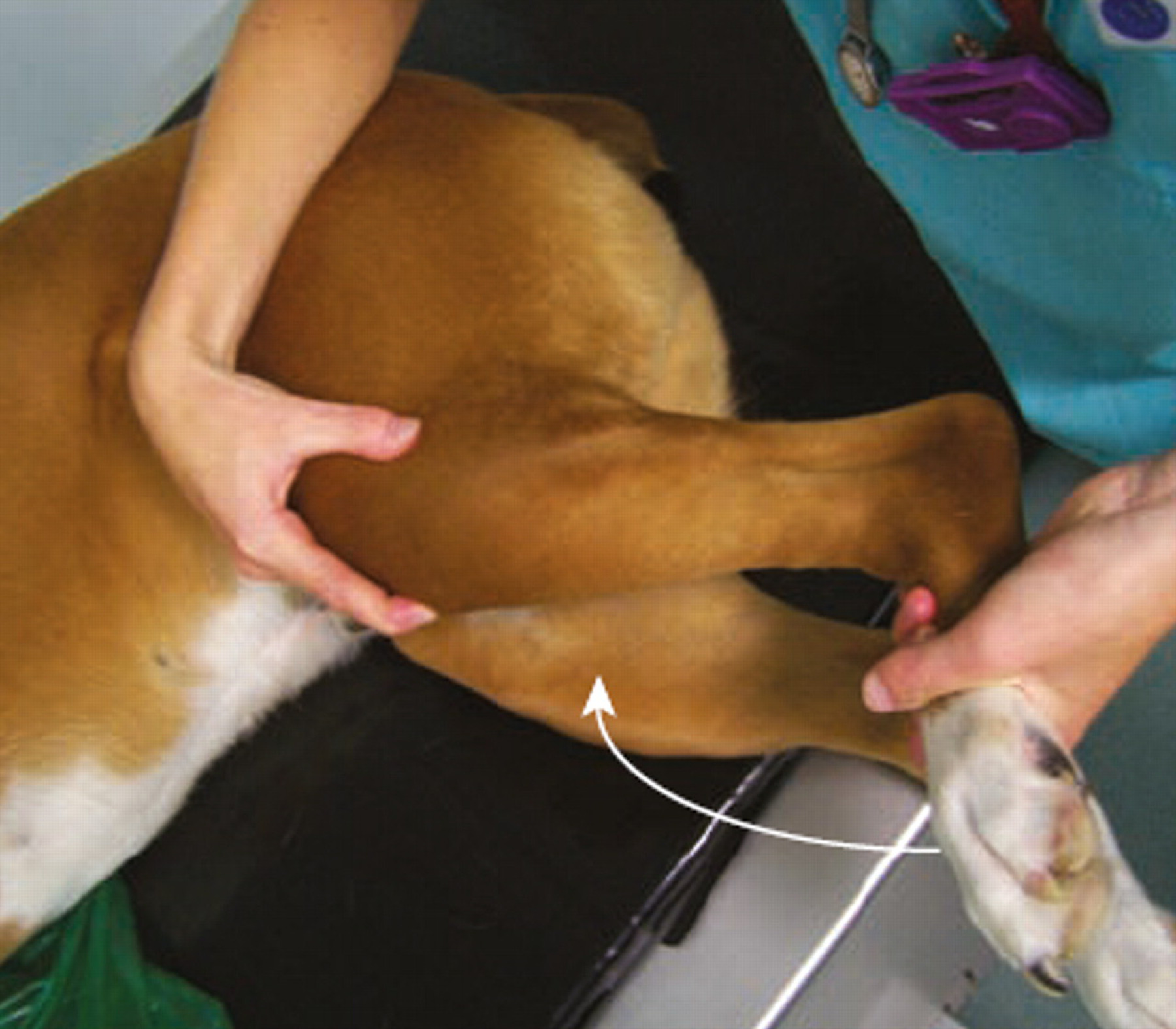
Article
Meniscal Tears in Dogs With Cranial Cruciate Ligament Rupture: Clinical Implications for Practitioners
Introduction Cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) rupture is a leading cause of stifle in...
